The Implementation Playbook for Instructionally Supportive Systems
Why an Implementation Playbook Is Needed
Many districts recognize the potential of instructionally supportive systems but struggle to operationalize the idea. This playbook offers a practical roadmap—from vision to classroom practice—to make that transformation real.
Instructionally supportive systems align assessment, instruction, and professional learning so every piece of data informs next steps for students and teachers alike.
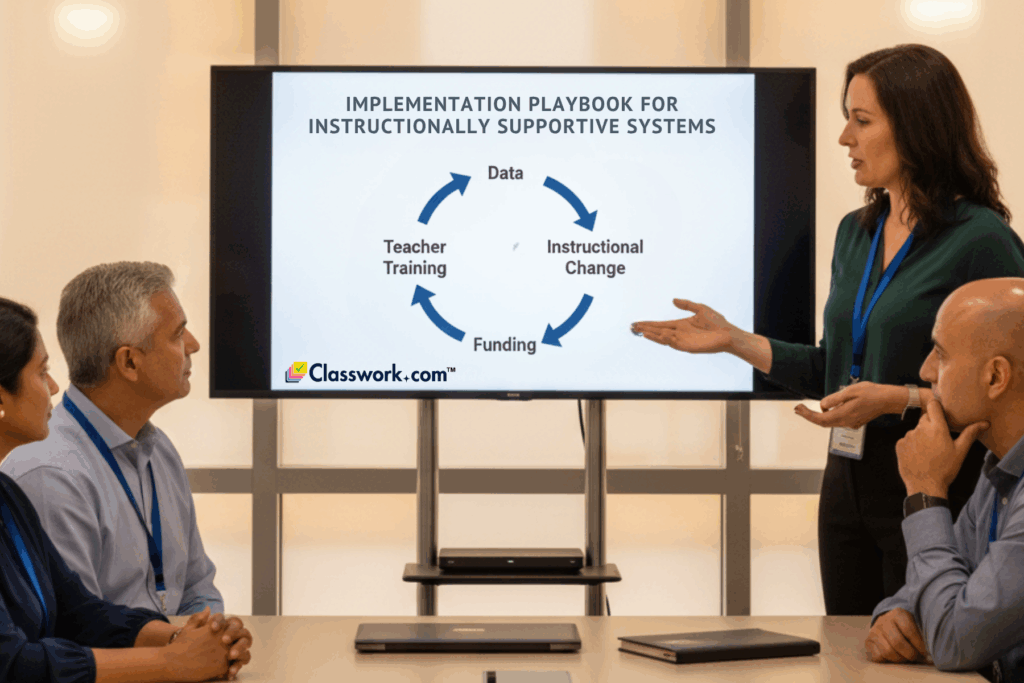
Step One: Establish the Vision
Start with the question: How will our system help teachers teach better tomorrow than they did today?
A clear vision ensures technology, data, and policies serve instruction—not the other way around.
Step Two: Build the Infrastructure
Data interoperability is key. Systems must connect:
- Classroom assessment platforms like Classwork.com,
- Curriculum management tools, and
- State reporting frameworks.
When teachers and administrators see the same data in context, collaboration becomes natural.
Step Three: Train for Instructional Decision-Making
Data literacy is now a core professional skill. Training should focus on:
- Interpreting daily data for immediate action,
- Using evidence to plan reteach cycles, and
- Applying data to differentiate instruction.
Classwork.com supports this by visualizing mastery and misconception patterns instantly.
Step Four: Embed Continuous Improvement
Instructionally supportive systems depend on ongoing feedback loops. Regular review cycles—weekly for PLCs, quarterly for leadership teams—ensure that decisions are evidence-based and adaptable.
Step Five: Integrate Professional Learning
Instructionally supportive systems use data not only to guide students, but to guide teacher learning. When data reveals common instructional challenges, districts can target PD sessions accordingly.
Student learning data should drive teacher learning.
Classwork.com enables this by aggregating classroom data across teachers and standards, revealing patterns that inform coaching and training.
Step Six: Sustain the Culture
Systemic change takes time. Districts must embed new routines into daily operations—protecting collaboration time, celebrating instructional wins, and using data for coaching rather than compliance.
When educators trust the system, they use it to grow.
Step Seven: Align Policy and Funding
True alignment requires that budgeting, scheduling, and accountability policies all support the same goal: instruction that responds to evidence.
State agencies, BOCES, and regional service centers can reinforce this shift by funding initiatives that bridge instruction and assessment.
Step Eight: Close the Loop—Data-Informed PD
The final step is closing the loop between student and teacher learning. Districts must use data not just to identify student needs but to identify instructional needs across classrooms.
By doing so, professional learning becomes as adaptive as student learning—responsive, evidence-based, and continuous.
Conclusion
Instructionally supportive systems don’t replace teaching—they make it visible.
They transform how educators use time, data, and collaboration to sustain growth.
Classwork.com was purpose-built for this new era—integrating instruction, feedback, and professional learning into a single, actionable ecosystem.
References
- Center for Assessment. (2024). Instructionally Supportive Systems: Implementation Considerations. https://naeducation.org/reimagining-balanced-assessment-systems-project/
- Texas Education Agency. (2023). Effective Schools Framework. https://tea.texas.gov/ESF
- Fullan, M., & Quinn, J. (2016). Coherence: The Right Drivers in Action for Schools, Districts, and Systems. Corwin. https://michaelfullan.ca/books/coherence-right-drivers-action-schools-districts-systems/
This article is part of The Future of Instructionally Supportive Assessment white paper. Read the full series here.
Quick Summary & Common Questions
What is the core purpose of an “Instructionally Supportive System”? An instructionally supportive system is designed to align assessment, instruction, and professional learning into a single, cohesive roadmap. The goal is to ensure that every piece of classroom data collected is actionable, directly informing the next instructional steps for teachers and personalized learning paths for students.
How does data interoperability improve school district operations? Data interoperability allows separate platforms—such as Classwork.com, curriculum management tools, and state reporting frameworks—to “talk” to one another. When these systems are connected, administrators and teachers can view student performance in context, reducing manual data entry and allowing for more natural, evidence-based collaboration.
Why should student learning data drive professional development (PD)? By aggregating classroom data, districts can identify specific instructional challenges that are common across multiple classrooms or grade levels. This allows leadership to “close the loop” by targeting PD sessions to meet the actual needs of teachers, making professional learning as adaptive and responsive as student learning.
What are the most critical steps for sustaining a data-informed culture? Sustaining this culture requires moving beyond “data for compliance” and instead using data for coaching and growth. Key steps include protecting dedicated time for teacher collaboration (PLCs), establishing weekly and quarterly feedback loops, and ensuring that district policies and funding are specifically aligned to support instructionally responsive practices.

